Use Cases
Possible use cases are:
Execute graphs in chain
For example, we have to execute graph B, only if another graph A finished without any error.
So there is a relation between these graphs.
We can achieve this behavior by creating a graph event listener.
We create a listener for graph finished OK event of graph A
and choose an execute graph task type with graph B specified for execution.
If we create another listener for graph B with the execute graph task with graph C specified,
it will work as a chain of graphs.
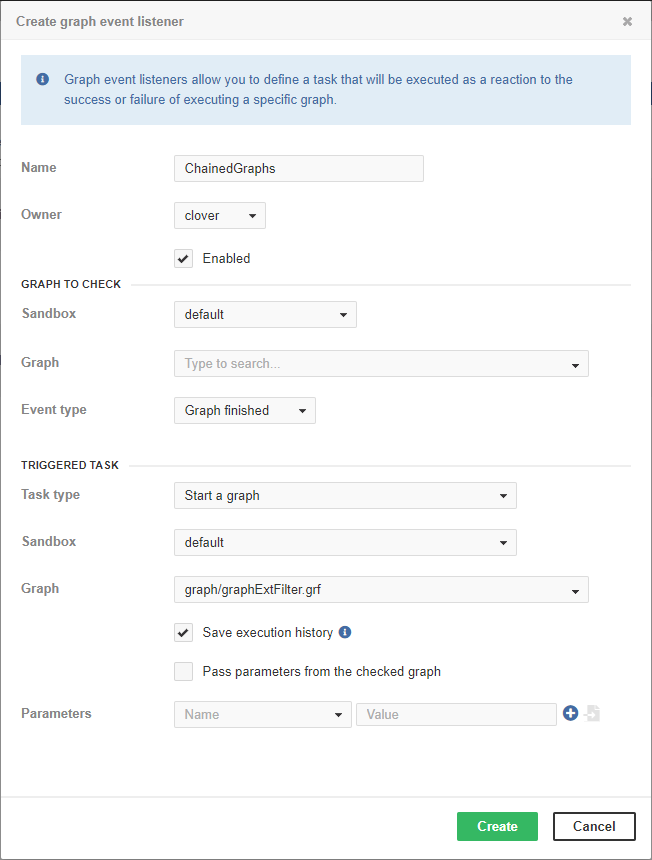
Figure 32.2. The event source graph isn't specified, thus the listener works for all graphs in the specified sandbox
Email notification about graph failure
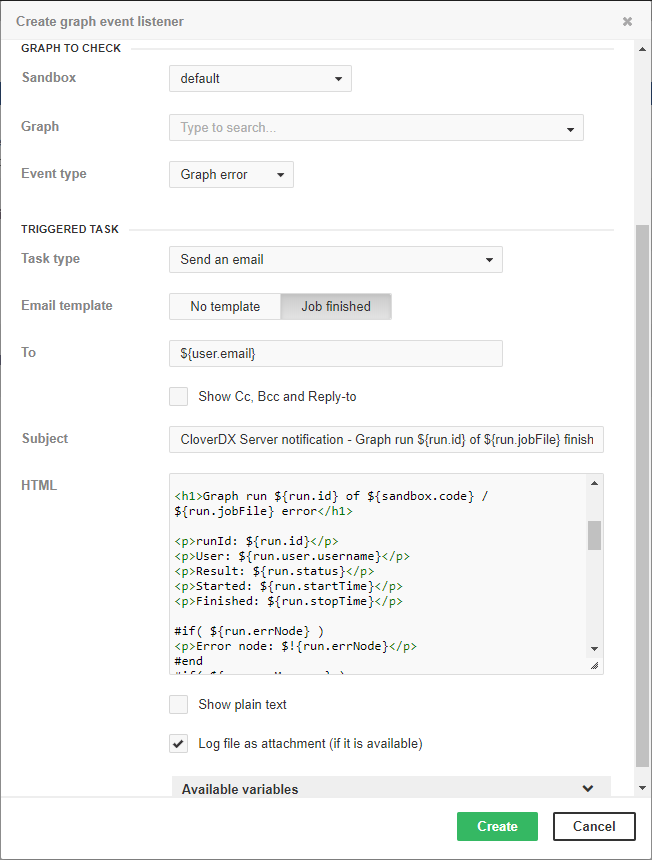
Figure 32.3. Web GUI - email notification about graph failure
Email notification about graph success
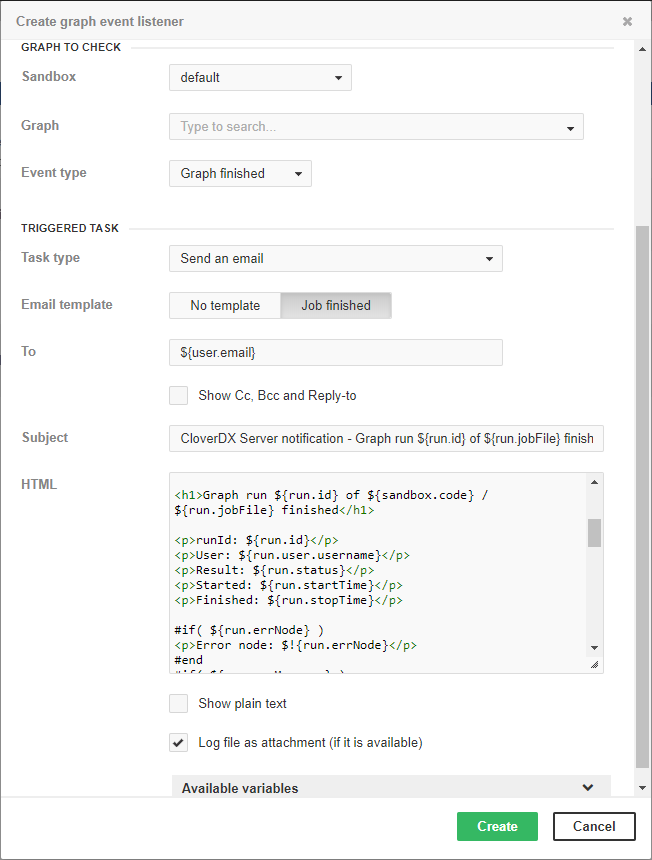
Figure 32.4. Web GUI - email notification about graph success
Backup of data processed by graph
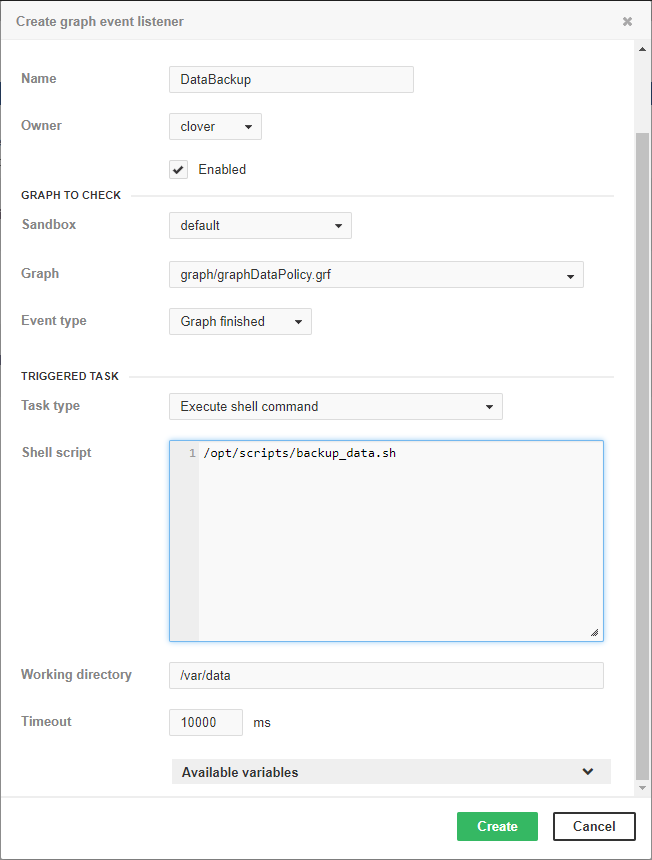
Figure 32.5. Web GUI - backup of data processed by graph
