JSONExtract

| Short Description |
| Ports |
| Metadata |
| JSONExtract Attributes |
| Details |
| Examples |
| Best Practices |
| Compatibility |
| See also |
Short Description
JSONExtract reads data from JSON files using SAX technology. It can also read data from compressed files, input port, and dictionary.
| Component | Data source | Input ports | Output ports | Each to all outputs | Different to different outputs | Transformation | Transf. req. | Java | CTL | Auto-propagated metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JSONExtract | JSON file | 0-1 | 1-n | ⨯ | ✓ | ⨯ | ⨯ | ⨯ | ⨯ | ⨯ |
Ports
| Port type | Number | Required | Description | Metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | 0 | ⨯ | For port reading. See Reading from Input Port. | One field (byte, cbyte, string). |
| Output | 0 | ✓ | For correct data records | Any |
| 1-n | [2] | For correct data records | Any | |
[2] Other output ports are required if mapping requires that. | ||||
Metadata
JSONExtract does not propagate metadata.
JSONExtract has no metadata template.
Metadata on optional input port must contain string
or byte or cbyte field.
Metadata on each output port does not need to be the same.
Each metadata can use Autofilling Functions.
JSONExtract Attributes
| Attribute | Req | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | |||
| File URL | yes | Attribute specifying what data source(s) will be read (JSON file, input port, dictionary). See Supported File URL Formats for Readers. | |
| Charset | Encoding of records which are read. | any encoding, default system one by default | |
| Mapping | [1] | Mapping of the input JSON structure to output ports. For more information, see XMLExtract Mapping Definition. | |
| Mapping URL | [1] | Name of an external file, including its path which defines mapping of the input JSON structure to output ports. For more information, see XMLExtract Mapping Definition. | |
| Equivalent XML Schema | URL of a file that should be used for creating the Mapping definition. For more information, see JSONExtract Mapping Editor and XSD Schema. | ||
| Use nested nodes |
By default, nested elements are also mapped to output ports automatically.
If set to | true (default) | false | |
| Trim strings |
By default, white spaces from the beginning and the end of the elements values are removed.
If set to | true (default) | false | |
| Advanced | |||
| Number of skipped mappings | Number of mappings to be skipped continuously throughout all source files. See Selecting Input Records. | 0-N | |
| Max number of rows to output | Maximum number of records to be read continuously throughout all source files. See Selecting Input Records. | 0-N | |
[1] One of these must be specified. If both are specified, Mapping URL has higher priority. | |||
Details
JSONExtract reads data from JSON files using SAX technology. This component is faster than JSONReader which can read JSON files too. JSONExtract does not use DOM, so it uses less memory than JSONReader.
JSONExtract can read lists.
JSONExtract can convert JSON to variant. Result variant can contain field/array values of following data types - null, string, boolean, long and number.
![[Note]](../figures/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
JSONExtract is very similar to XMLExtract.
JSONExtract internally transforms JSON to XML
and uses XMLExtract to parsing the data.
Therefore, you can generate |
Mapping in JSONExtract is almost same as in XMLExtract. The main difference is, that JSON does not have attributes. For more information, see XMLExtract's Details.
JSONExtract Mapping Editor and XSD Schema
JSONExtract Mapping Editor serves to set up mapping from JSON tree structure to one ore more output ports without the necessity of being aware how to create mapping of field using an XML editor.
To be able to use the editor, the editor needs to have created equivalent xsd schema. The equivalent xsd schema is created automatically. Only the directory for the schema needs to be specified.
Any other operations to set up mapping are described in above mentioned XMLExtract.
Mapping Input Fields to the Output Fields
In JSONExtract, you can map input fields to the output in the same way as you map JSON fields. The input field mapping works in all three processing modes.
Examples
Reading lists
JSON file contains information about employees and orders. Each item contains employee ID and list of order IDs.
{
"jsonextract_order" : {
"employee" : "Henri",
"orders" : [ "order01", "order08", "order15" ]
},
"jsonextract_order" : {
"employee" : "Jane",
"orders" : [ "order02", "order05", "order09" ]
}
}Read data for further processing.
Solution
Use the File URL attribute to point to the source file and the Mapping attribute to define mapping.
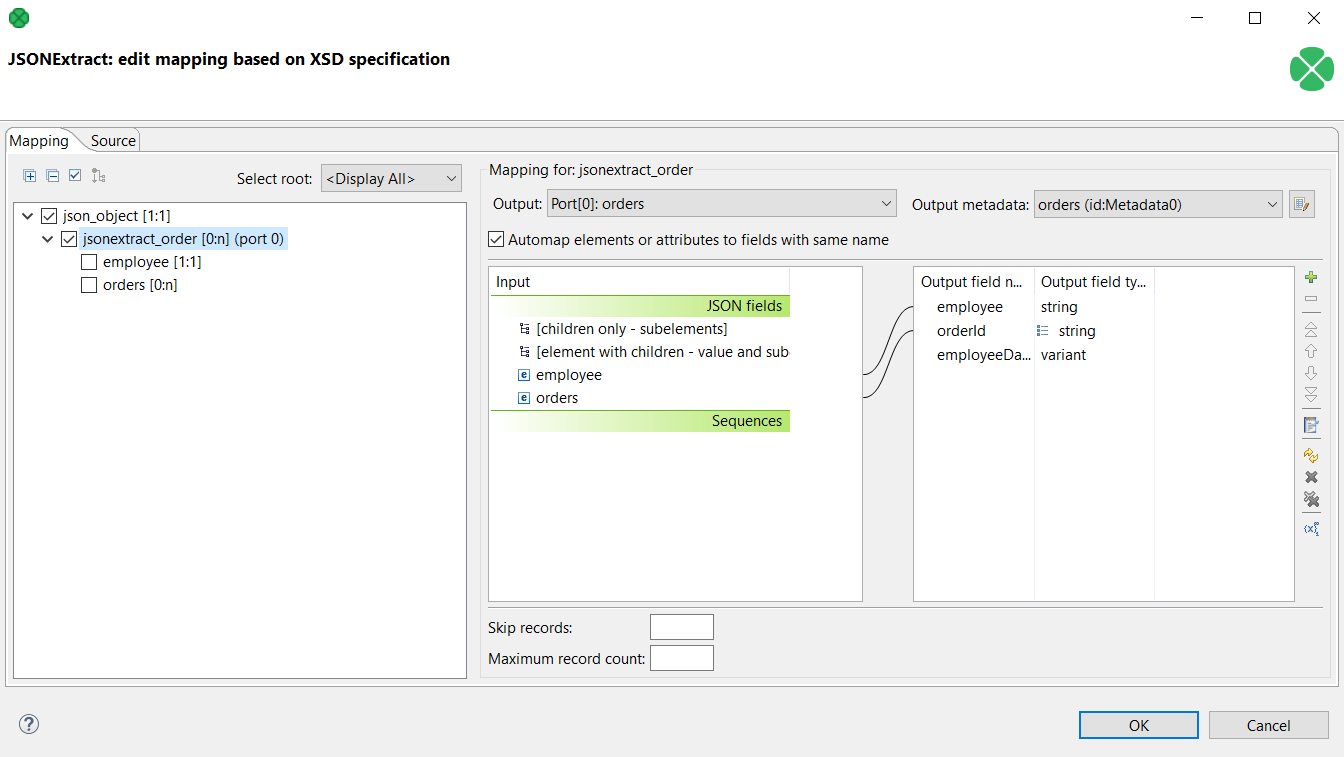 |
Figure 55.15. JSONExtract - mapping the list
Reading variants
JSON file contains information about employees and orders. Each item contains employee ID and list of order IDs.
{
"jsonextract_order" : {
"employee" : "Henri",
"orders" : [ "order01", "order08", "order15" ]
},
"jsonextract_order" : {
"employee" : "Jane",
"orders" : [ "order02", "order05", "order09" ]
}
}Read data for further processing.
Solution
Use the File URL attribute to point to the source file and the Mapping attribute to define mapping.
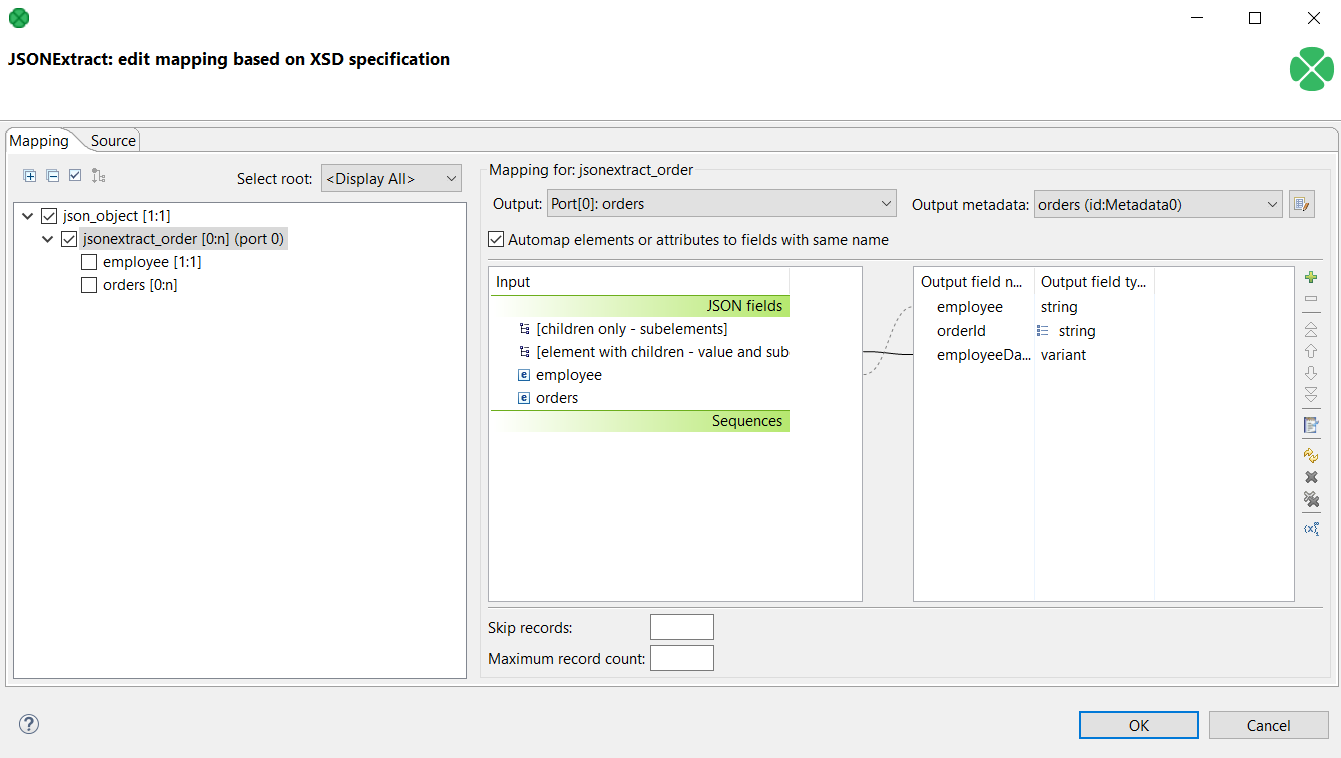 |
Figure 55.16. JSONExtract - mapping the variant
Content of mapped output variant field depends on structure of input JSON.
// for the first input element $out.0.employeeData["jsonextract_order"]["employee"]; // contains 'Henri' $out.0.employeeData["jsonextract_order"]["orders"][0]; // contains 'order01'
Best Practices
We recommend users to explicitly specify Charset.
Compatibility
| Version | Compatibility Notice |
|---|---|
| 3.5.0-M2 | JSONExtract is available since 3.5.0-M2. |
| 4.1.0-M1 | You can now map input fields to the output fields in this component. |
| 4.1.0 | You can now read lists. |
| 5.11.0 | You can now extract JSON to variant. |
| 5.11.0 | Null values are no longer converted to an empty string on output. |
