Database Connection Properties
The Database Connection Properties dialog lets you configure particular properties of a database connection. In the dialog, you can choose a JDBC driver or an existing JNDI resource, set up credentials, transaction isolation level, etc.
You can create a database connection that uses a user-defined JDBC Driver or a JNDI Resource.
| JDBC driver |
| JNDI resource |
JDBC driver
| Basic Properties of JDBC driver |
| Generic ODBC |
| Microsoft Access |
| Microsoft Access ODBC |
| Advanced Properties of JDBC driver |
The dialog consists of two tabs: Basic properties and Advanced properties.
Basic Properties of JDBC driver
In the Basic properties tab of JDBC driver in the Database connection dialog, you specify the name of the connection, type your User name, your access Password and URL of the database connection (hostname, database name or other properties).
The password can be encrypted using Secure Graph Parameters.
JDBC Specific
The default JDBC specific can be used, but the specific one might suit your purpose better. By setting JDBC specific, you can slightly change the behavior of the connection such as different data type conversion, getting auto-generated keys, etc.
Database connection is optimized according to this attribute. JDBC specific adjusts the connection for the best cooperation with the given type of database.
You can also choose from the following connections built in CloverDX: Derby, Firebird, Microsoft SQL Server (for Microsoft SQL Server 2008 or Microsoft SQL Server 2000-2005 specific), MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, Sybase and SQLite.
After selecting one of them, you can see in the connection code one of the following expressions:
database="DERBY", database="FIREBIRD",
database="MSSQL", database="MYSQL",
database="ORACLE", database="POSTGRE",
database="SYBASE" or database="SQLITE", respectively.
![[Important]](../figures/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
If you need to connect to ODBC resources, use the Generic ODBC driver. However, choose it only if other direct JDBC drivers do not work. Moreover, mind using a proper ODBC version which suits your CloverDX - either 32 or 64-bit. |
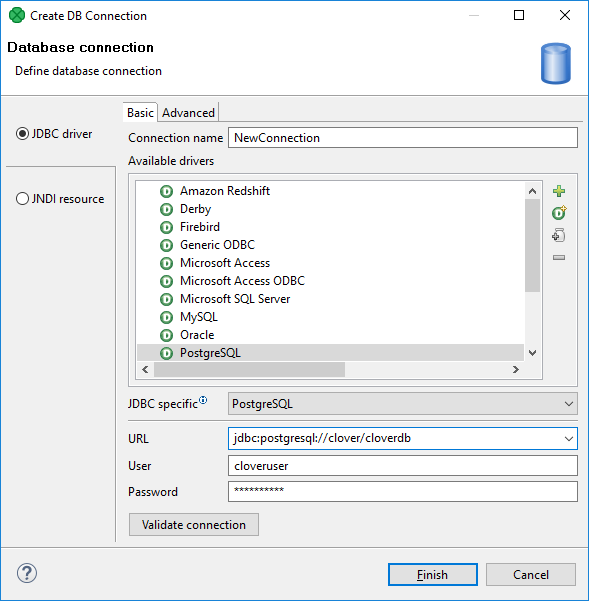
Figure 33.1. Database Connection Properties Dialog
Adding JDBC Drivers and Jars
If you want to use some other driver,
you can use one of the Available drivers.
If the desired JDBC driver is not in the list,
you can add it by clicking the
![]() sign located on the right side of the dialog (Load driver from JAR).
Then you can locate the driver and confirm its selection.
sign located on the right side of the dialog (Load driver from JAR).
Then you can locate the driver and confirm its selection.
If necessary, you can also add another JAR to the driver classpath (). For example, some databases may need their license to be added as well as the driver.
JDBC Drivers
CloverDX has built-in JDBC drivers for: Derby, Firebird, Microsoft SQL Server 2008, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, SQLite and Sybase databases. You can choose any JDBC driver from the list of available drivers.
By clicking any driver, a connection string hint appears in the URL text area. You only need to modify the connection.
You can also specify JNDI.
![[Important]](../figures/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
Remember that CloverDX supports JDBC 3 drivers and higher. |
Once you have selected the driver from the list,
you only need to type your username and password for connecting to the database.
You also need to change the hostname to its correct name.
Type the right database name instead of the database filler word.
Some other drivers provide different URLs that must be changed in a different way.
You can also load an existing connection from one of the existing configuration files.
You can set up the JDBC specific property, or use the default one; however, it may not do all that you want. By setting JDBC specific you can slightly change the selected connection behavior such as different data type conversion, getting auto-generated keys, etc.
Database connections are optimized based on this attribute. JDBC specific adjusts the connection for the best cooperation with the given type of database.
Note that you can also remove a driver from the list in the Basic tab () and custom properties in the Advanced tab () by clicking the sign on the respective tab.
Generic ODBC
The Generic ODBC driver reads data sources which are not directly listed in Available drivers (e.g. DBF).
To connect to ODBC resources:
Click the Generic ODBC driver.
Specify the
dsn_sourcein URL. In Windows, this is what you can see in → as Name.Leave fields User and Password blank.
Notes on using Generic ODBC driver
In DatabaseWriter, mapping of metadata fields to SQL fields cannot be checked. Make sure the mapping is designed correctly. If the mapping is invalid, the graph fails.
You cannot set any transaction isolation level (a warning appears in the log).
![[Important]](../figures/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
Choose Generic ODBC only if other direct JDBC drivers do not work. Even if the ODBC driver exists, it does not necessarily have to work in CloverDX (which was successfully tested with MySQL ODBC driver). Moreover, mind using a proper ODBC version which suits your CloverDX - either 32 or 64-bit. |
Microsoft Access
This driver internally uses the UCanAccess driver. CloverDX uses version 4.0.2. See the offical UcanAccess webpage.
In DatabaseWriter,
longtype cannot be used in input metadata. Consider using Reformat in your graph to convertlongfields to other metadata types.booleanfields that arenullwill be actually written asfalse(null value is not supported).You cannot write
nullintobinaryfields, either.By default, CloverDX uses the
singleconnection=trueproperty of the UCanAccess driver to minimize usage of system resources. This default can be overridden in connection URL or in Custom JDBC properties. For more details on driver properties, see the driver's documentation.
![[Important]](../figures/important.png) | Important |
|---|---|
MS Access data type NUMBER with field size INTEGER corresponds to SQL_SMALLINT, which can only hold values between approximately -32,000 and +32,000. If you store any value that would overflow this data type field, UCanAccess driver does not report the overflow and saves overflown (incorrect) value. Check the value before insertion or use ODBC driver which can detect the error. |
![[Note]](../figures/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
Introduced in version 4.0.7. |
Microsoft Access ODBC
The driver supposes you have default MS Access drivers installed (check if there is MS Access Database in → ). Next steps:
Click Microsoft Access ODBC in Available drivers.
URL - replace
database_filewith absolute path to your MDB file.
Notes on using Microsoft Access ODBC driver:
In DatabaseWriter,
longanddecimaltypes cannot be used in input metadata. Consider using Reformat in your graph to convert these to other metadata types. Use Microsoft Access driver to write decimals.In DatabaseWriter, mapping of metadata fields to SQL fields cannot be checked. Make sure the mapping is designed correctly. If the mapping is invalid, the graph fails.
You cannot set any transaction isolation level (a warning appears in the log).
booleanfields that arenullwill be actually written asfalse(null value is not supported).You cannot write
nullintobinaryfields, either.
This driver was renamed in version 4.0.7. The original name was MS Access.
Advanced Properties of JDBC driver
| Thread-safe connection |
| Transaction isolation |
| Holdability |
In addition to the Basic properties tab described above, the Database connection dialog also offers the Advanced properties tab.
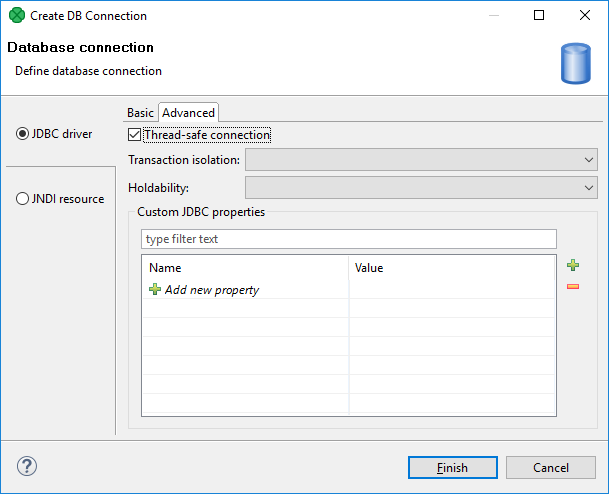
Figure 33.2. Advanced tab of the Database connection dialog
If you switch to this tab, you can specify some other properties of the selected connection:
Thread-safe connection
By default, it is enabled. In this default setting, each thread gets its own connection to prevent problems when more components converse with DB through the same connection object which is not thread safe.
Transaction isolation
Allows to specify certain transaction isolation level. More details can be found here: Interface Connection. Possible values of this attribute are:
0(TRANSACTION_NONE).A constant indicating that transactions are not supported.
1(TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED).A constant indicating that dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads can occur. This level allows a row changed by one transaction to be read by another transaction before any changes in that row have been committed (a "dirty read"). If any of the changes are rolled back, the second transaction will have retrieved an invalid row.
This is the default value for DB2, Derby, EXASolution, Informix, MySQL, MS SQL Server 2008, MS SQL Server 2000-2005, PostgreSQL and SQLite specifics.
This value is also used as default when JDBC specific called Generic is used.
2(TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED).A constant indicating that dirty reads are prevented; non-repeatable reads and phantom reads can occur. This level only prohibits a transaction from reading a row with uncommitted changes in it.
This is the default value for Oracle, Sybase and Vertica specifics.
4(TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ).A constant indicating that dirty reads and non-repeatable reads are prevented; phantom reads can occur. This level prohibits a transaction from reading a row with uncommitted changes in it, and it also prohibits a situation where one transaction reads a row, a second transaction alters the row and the first transaction rereads the row, getting different values the second time (a "non-repeatable read").
8(TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE).A constant indicating that dirty reads, non-repeatable reads and phantom reads are prevented. This level includes the prohibitions in
TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READand further prohibits a situation where one transaction reads all rows that satisfy awherecondition, a second transaction inserts a row that satisfies thewherecondition and the first transaction rereads for the same condition, retrieving the additional "phantom" row in the second read.
Holdability
Allows to specify holdability of ResultSet objects
created using the Connection.
More details can be found here:
Interface ResultSet.
Possible options are the following:
1(HOLD_CURSORS_OVER_COMMIT).The constant indicating that
ResultSetobjects should not be closed when the methodConnection.commitis called.This is the default value for Informix and MS SQL Server 2008 specifics.
2(CLOSE_CURSORS_AT_COMMIT).The constant indicating that
ResultSetobjects should be closed when the methodConnection.commitis called.This is the default value for DB2, Derby, MS SQL Server 2000-2005, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Sybase and Vertica specifics.
This value is also used as default when JDBC specific called Generic is used.
JNDI resource
In the JNDI resource tab, you can create a connection from an existing JNDI resource.
JNDI is a configuration used to obtain a connection from a JNDI-bound data source. A data source generates database connections from a connection pool which is defined on the level of an application server.
Basic Properties
In Basic tab of JNDI resource, you can name the database connection and choose a corresponding database JNDI resource from the tree-view.
Connection name is a user-defined name of the database connection.
JDBC specific is described in JDBC driver.
JNDI name is a name of a JNDI data source. If you choose a particular JNDI data source from the tree-view below, JNDI name is filled in.
Root context allows you to choose root context of JNDI resource. You can choose one of the pre-filled values: java:comp, java:comp/env and <empty>, or you can add your own value: click the combo, type the value, and press Enter.
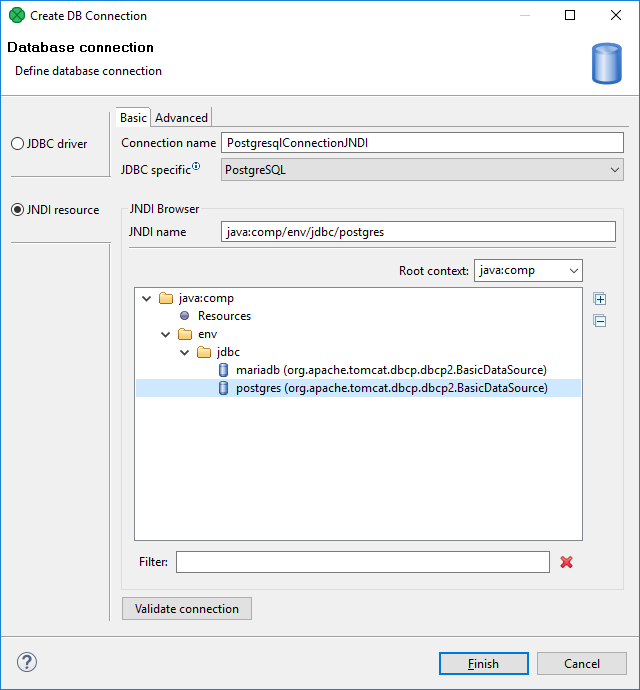
Figure 33.3. JNDI resource - Basic tab
To create a database connection, specify the Connection name and choose the database JNDI resource from the tree-view. If there are too many resources, Filter might help you.
![[Note]](../figures/note.png) | Note |
|---|---|
If you have configured JNDI resource but you cannot see it in the list, there can be a problem with configuration (e.g. typo or bad password) or the database might refuse the resource to connect due to limit on connections. You can enter the JNDI Name and use the connection to see the cause. |
Advanced Properties
The advanced tab of JNDI resource has the same configurable items as the advanced tab of JDBC driver. See Advanced Properties of JDBC driver.
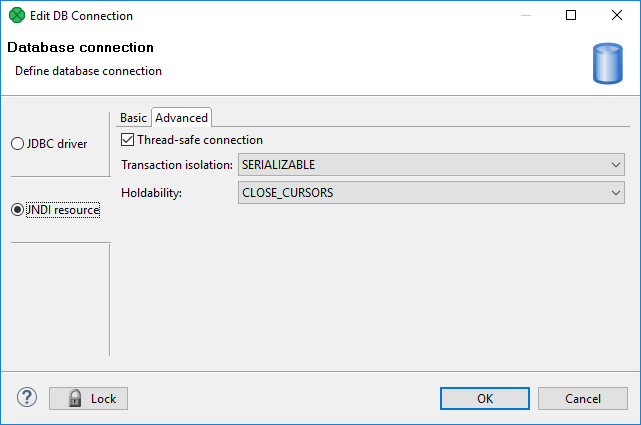
Figure 33.4. JNDI resource - Basic tab
