EDIWriter

| Short Description |
| Ports |
| Metadata |
| EDIWriter Attributes |
| Details |
| Examples |
| See also |
Short Description
EDIWriter writes data in the EDIFACT format.
All EDIFACT versions from D.93A to D.21A are supported.
EDIWriter is currently only available to selected OEM partners. To find out more, please contact
sales@cloverdx.com.
| Component | Data output | Input ports | Output ports | Transformation | Transf. req. | Java | Auto-propagated metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDIWriter | EDIFACT interchange | 1-n | 0-1 | ⨯ | ⨯ | ⨯ | ⨯ |
Ports
| Port type | Number | Required | Description | Metadata |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | 0-N | At least one | Input records to be mapped into the EDIFACT message structure. | Any (each port can have different metadata) |
| Output | 0 | ⨯ | For port writing. |
Only one field (byte, cbyte or string) is used.
The field name is used in File URL
to govern how the output records are processed -
see Writing to Output Port
|
Metadata
EDIWriter does not propagate metadata.
EDIWriter has no metadata template.
EDIWriter Attributes
| Attribute | Req | Description | Possible values |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic | |||
| File URL | yes | The target file for the output EDIFACT message. See Supported File URL Formats for Writers. | |
| EDIFACT version | Attribute specifying version of EDIFACT message. | ||
| EDIFACT message | Attribute specifying type of EDIFACT message. Possible values depend on selected EDIFACT version. | ||
| Interchange sender identification |
Attribute specifying default identification of EDIFACT interchange sender.
When specified, the value is used as default for | ||
| Interchange recipient identification |
Attribute specifying default identification of EDIFACT interchange recipient.
When specified, the value is used as default for | ||
| Interchange control reference |
Attribute specifying default identification of EDIFACT interchange.
When specified, the value is used as default for | ||
| Message reference number |
Attribute specifying default identification of EDIFACT message.
When specified, the value is used as default for | ||
| Mapping | [1] | Defines how input data is mapped onto an output EDIFACT message. See Details. | |
| Mapping URL | [1] | External text file containing the mapping definition. | |
| Advanced | |||
| Cache size | The size of the database used when caching data from ports to elements (the data is first processed then written). The larger your data is, the larger cache is needed to maintain fast processing. | auto (default) | e.g. 300MB, 1GB etc. | |
| Cache in Memory |
Cache data records in memory instead of the JDBM's disk cache (default).
Note that while it is possible to set the maximal size of the disk cache,
this setting is ignored in case the in-memory cache is used.
As a result, an | false (default) | true | |
| Sorted input | Tells EDIReader whether the input data is sorted. Setting the attribute to true declares you want to use the sort order defined in Sort keys, see below. | false (default) | true | |
| Sort keys | Tells EDIReader how the input data is sorted, thus enabling streaming. The sort order of fields can be given for each port in a separate tab. Working with Sort keys has been described in Sort Key. | ||
[1] One of these must be specified if EDIFACT version and EDIFACT message are used. If both are specified, Mapping URL has a higher priority. | |||
Details
EDIWriter receives data from all connected input ports and converts records to EDIFACT message structure based on the mapping you define. Finally, the component writes the resulting tree structure of elements to the output: an EDIFACT message file, port or dictionary.
Input data has to provide all mandatory data required by selected EDIFACT message format. When any mandatory element is missing the mapping editor produces a warning. Type of a message can be specified by EDIFACT version and EDIFACT message properties in the component.
Individual fields of EDIFACT message can be filled by input fields of primitive types such as string or long. Entire subtrees of the target message can be filled by input variant fields. When using variant fields the structure of the input variant must match the schema of the target mapped element, otherwise the EDIWriter will fail at runtime.
Specifying EDIFACT version and EDIFACT message is optional. You can leave both attributes empty, in which case EDIWriter expects a single variant field with entire interchange structure on first input port. The expected structure is the same as produced by EDIReader. Defining a mapping is not possible in this case.
Examples
Mapping different ports on parts of an EDIFACT message format allows to insert multiple repeating segments into one EDIFACT message file.
The example below creates one EDIFACT interchange for each record obtained from port 0 and one AUTHOR message for each record obtained from port 2.
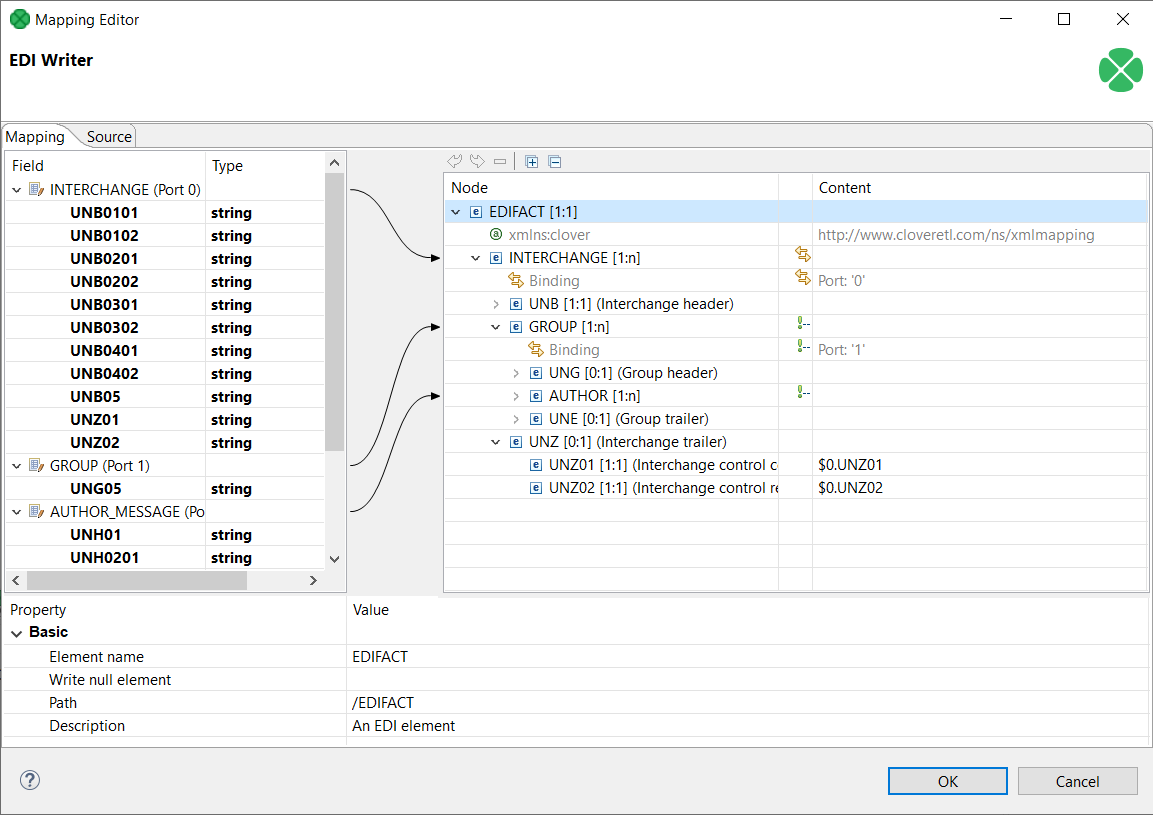 |
Figure 56.4. EDIReader - mapping input records on different parts of a message
Compatibility
| Version | Compatibility Notice |
|---|---|
| 5.13 |
EDIWriter is available since 5.13.0. |
